Introduction:
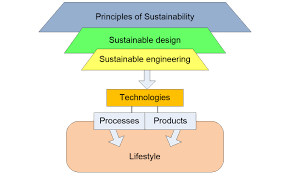
As stewards of the built environment, civil engineers play a pivotal role in shaping sustainable communities and infrastructure systems. Sustainable design principles guide engineers in creating solutions that balance environmental, social, and economic considerations, aiming to minimize negative impacts on the planet while maximizing benefits for current and future generations. In this blog, we’ll delve into the core sustainable design principles that civil engineers should embrace to create resilient, efficient, and environmentally-friendly infrastructure.
1. Integration of Green Infrastructure:
Green infrastructure involves incorporating natural elements and processes into the design and planning of infrastructure projects to enhance environmental sustainability and resilience. Civil engineers can integrate green infrastructure elements such as vegetated swales, rain gardens, green roofs, and permeable pavements to manage stormwater, improve air and water quality, and enhance biodiversity. By mimicking natural ecosystems and promoting ecosystem services, green infrastructure mitigates the urban heat island effect, reduces flood risk, and enhances the overall health and well-being of communities.
2. Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy:
Incorporating energy-efficient design strategies and renewable energy technologies is essential for reducing the carbon footprint of infrastructure projects and mitigating climate change. Civil engineers can optimize building orientation, insulation, and passive solar design to minimize energy consumption and maximize natural daylighting and ventilation. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources such as solar photovoltaics, wind turbines, and geothermal heating and cooling systems can further reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote a transition to clean, renewable energy sources.
3. Optimal Use of Resources:
Sustainable design principles emphasize the efficient use of resources, including materials, water, and land, throughout the project lifecycle. Civil engineers can adopt strategies such as material reuse, recycling, and salvaging to minimize construction waste and conserve natural resources. Additionally, implementing water-saving technologies, such as low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater reuse systems, can reduce water consumption and promote water efficiency in buildings and infrastructure. By optimizing land use and promoting compact, walkable development patterns, engineers can minimize urban sprawl, preserve green space, and enhance the livability of communities.
4. Resilience and Climate Adaptation:
Designing infrastructure with resilience and climate adaptation in mind is essential for ensuring long-term functionality and durability in the face of changing environmental conditions and extreme weather events. Civil engineers can integrate resilience measures such as flood-resistant design, coastal protection systems, and climate-responsive building envelopes to mitigate the impacts of climate change and natural hazards. By incorporating climate projections and risk assessments into the design process, engineers can future-proof infrastructure and enhance its ability to withstand a range of environmental stressors.
5. Community Engagement and Social Equity:
Sustainable design principles prioritize community engagement, social equity, and inclusivity, ensuring that infrastructure projects benefit all members of society. Civil engineers should actively engage with stakeholders, including residents, businesses, and marginalized communities, throughout the planning, design, and implementation stages to incorporate diverse perspectives and address community needs. Promoting accessibility, affordability, and safety in infrastructure design fosters social cohesion, improves quality of life, and promotes equitable access to essential services and amenities.
Case Studies:
1. The High Line, New York City, USA:
The High Line, an elevated linear park built on a disused railway viaduct in New York City, exemplifies sustainable design principles in urban redevelopment. The project transformed a derelict industrial site into a vibrant public space featuring greenery, pedestrian walkways, and community amenities. By integrating green infrastructure, adaptive reuse, and community engagement, the High Line revitalized the surrounding neighbourhood, improved urban connectivity, and promoted environmental sustainability.
2. Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, UAE:
Masdar City is a sustainable urban development project in Abu Dhabi, designed to be a model for low-carbon, resource-efficient living. The city incorporates passive solar design, renewable energy systems, and water-saving technologies to minimize environmental impact and reduce energy consumption. Through smart planning, compact urban design, and mixed land uses, Masdar City promotes social inclusion, economic prosperity, and environmental stewardship, demonstrating the potential of sustainable design principles in shaping the cities of the future.
Conclusion: