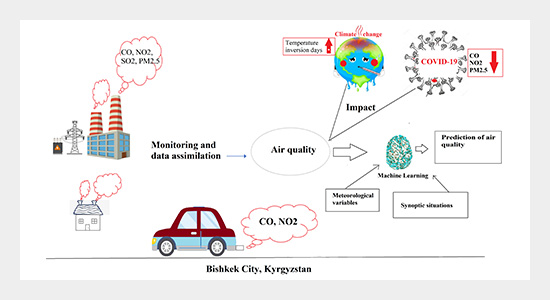
In our increasingly urbanized world, the quality of the air we breathe has become a critical concern. With rapid industrialization, urbanization, and vehicular emissions, air pollution has emerged as a major threat to public health and the environment. However, as we progress into the future, advancements in technology offer promising solutions to monitor and mitigate air pollution more effectively in urban areas.
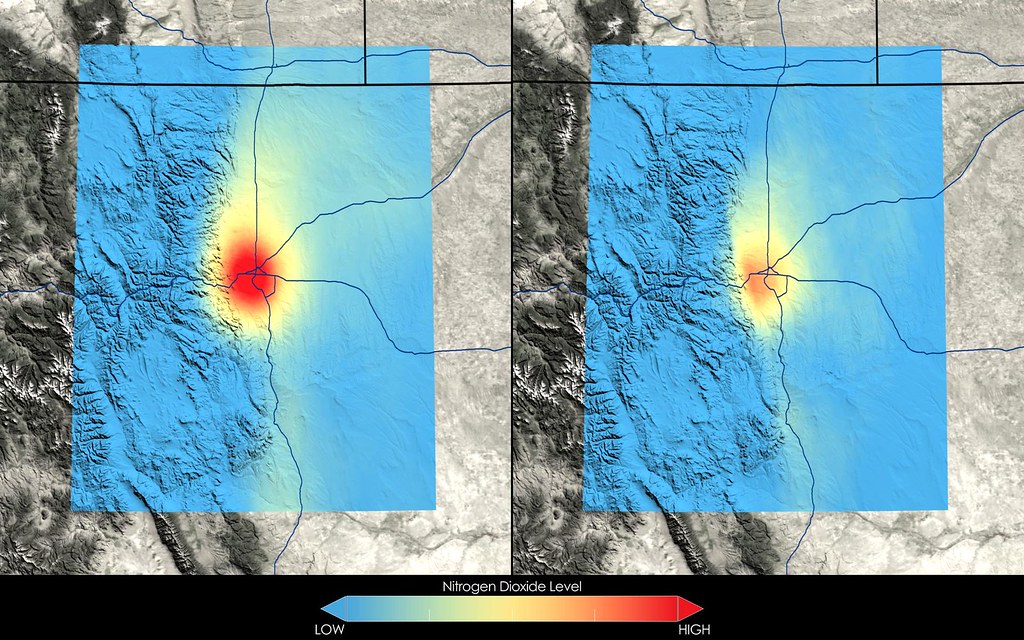
One of the most significant advancements lies in the development of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and sensor networks. These small, low-cost sensors can be deployed across urban landscapes to continuously monitor air quality in real-time. These sensors can measure various pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3). By providing granular data on pollution levels, these sensors enable policymakers, urban planners, and citizens to make informed decisions to improve air quality.
Moreover, the integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning algorithms enhances the capabilities of air quality monitoring systems. These algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected by sensors, identify pollution patterns, predict future trends, and even suggest optimal strategies for pollution control. Machine learning models can also correlate air quality data with other factors such as weather conditions, traffic patterns, and industrial activities to provide a more comprehensive understanding of pollution sources and dynamics in urban areas.
Furthermore, the emergence of mobile monitoring platforms and wearable devices empowers individuals to monitor their personal exposure to air pollution in real-time. Smartphone apps equipped with pollution sensors allow users to access localized air quality information and receive alerts when pollution levels exceed safe limits. Wearable air quality monitors, such as smartwatches or portable sensors, provide users with personalized insights into their immediate surroundings, enabling them to make informed decisions to minimize exposure to harmful pollutants.
In addition to technological innovations, the future of air quality monitoring also entails greater collaboration between governments, industries, academia, and communities. Public-private partnerships can facilitate the deployment of sensor networks, data sharing agreements, and the development of innovative solutions to address air pollution challenges. Citizen science initiatives empower communities to participate in data collection efforts, raise awareness about air quality issues, and advocate for policy changes to improve environmental sustainability.
Nevertheless, while technological advancements offer promising solutions for air quality monitoring in urban areas, challenges remain. Ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and calibration of sensor data is crucial to maintaining the credibility of monitoring systems. Additionally, addressing issues of data privacy, security, and equity in access to air quality information is essential to ensure that monitoring efforts benefit all segments of society.
In conclusion, the future of air quality monitoring in urban areas holds great promise, driven by advancements in technology, data analytics, and collaborative efforts. By leveraging IoT devices, AI algorithms, and citizen engagement, we can create more resilient and sustainable cities where everyone can breathe clean air and thrive. However, realizing this vision requires concerted action from governments, industries, and communities to prioritize environmental health and embrace innovative solutions for a cleaner, healthier future.