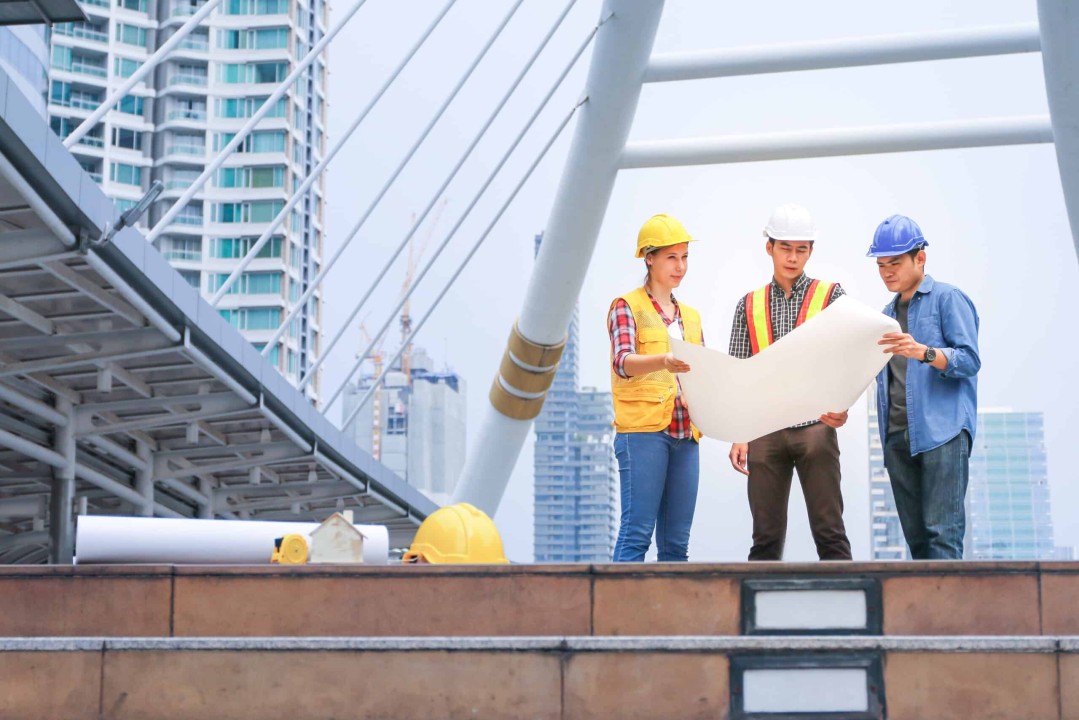
1. Infrastructure Development:
– In developing countries, infrastructure development is crucial for fostering economic growth, enhancing connectivity, and improving quality of life.
– Civil engineers are involved in a wide range of infrastructure projects, including transportation networks (roads, bridges, railways), energy systems (power plants, transmission lines), water supply and sanitation facilities, and telecommunications infrastructure.
– These projects create employment opportunities, attract investment, and stimulate economic activity in both urban and rural areas, contributing to poverty reduction and socioeconomic development.
2. Sustainable Urbanization:
– Rapid urbanization is a prominent trend in developing countries, with millions of people migrating from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities.
– Civil engineers play a critical role in managing urban growth and ensuring sustainable urban development by designing and implementing infrastructure solutions that meet the needs of growing urban populations while minimizing environmental impact.
– Sustainable urban infrastructure includes public transportation systems (such as buses, metro, and light rail), affordable housing developments, green spaces, and waste management facilities.
– Civil engineers integrate principles of urban planning, environmental sustainability, and social equity to create inclusive and resilient cities that can withstand the challenges of rapid urbanization, climate change, and natural disasters.
3. Access to Clean Water and Sanitation:
– Access to clean water and sanitation is a fundamental human right, yet millions of people in developing countries lack access to safe drinking water and adequate sanitation facilities.
– Civil engineers design and implement water supply and sanitation projects, including water treatment plants, distribution networks, sewage systems, and sanitation facilities, to improve public health outcomes and enhance quality of life.
– These projects often involve community engagement, capacity building, and awareness-raising initiatives to ensure sustainable operation and maintenance of water and sanitation infrastructure.
4. Disaster Risk Reduction and Resilience:
– Developing countries are disproportionately affected by natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, hurricanes, and droughts, which can cause significant loss of life, property damage, and disruption to critical infrastructure.
– Civil engineers play a crucial role in disaster risk reduction and resilience-building by designing infrastructure that can withstand natural hazards, implementing early warning systems, and developing emergency response plans.
– Resilient infrastructure includes measures such as reinforced buildings, flood-resistant roads, and decentralized water supply systems that can continue to function during and after disasters, minimizing the impact on communities and facilitating recovery efforts.
5. Technology and Innovation:
– Technology and innovation are transforming civil engineering practices in developing countries, enabling engineers to overcome traditional barriers and deliver more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions.
– Digital tools such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and remote sensing technologies are used to streamline project planning, design, and construction processes, improving accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
– Innovative approaches such as prefabricated construction techniques, renewable energy systems, and smart infrastructure solutions are being adopted to address emerging challenges and capitalize on opportunities for sustainable development.
Challenges and Strategies:
Despite the significant contributions of civil engineering to development, numerous challenges persist in developing countries, including inadequate funding, limited technical capacity, regulatory barriers, and political instability.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to prioritize investment in infrastructure, strengthen institutional capacity, foster public-private partnerships, and promote knowledge sharing and technology transfer.
Civil engineers must adopt a multidisciplinary and participatory approach, engaging with local communities, governments, academia, and international organizations to ensure the sustainability, equity, and inclusivity of infrastructure development efforts.
Conclusion:
Civil engineering is a driving force behind the transformation of developing countries, providing essential infrastructure and services that improve quality of life, stimulate economic growth, and foster sustainable development. By addressing pressing challenges, harnessing innovative technologies, and promoting collaboration and capacity building, civil engineers in developing countries can pave the way for a brighter and more prosperous future for all.