Introduction:
In the face of climate change and environmental degradation, sustainable development has become an imperative for modern society. From urban centers to rural landscapes, every facet of human development must be approached with an eye towards sustainability. One critical aspect of this approach is sustainable site development – the thoughtful planning, design, and construction of sites that minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and enhance the well-being of communities. In this blog, we delve into various sustainable site development strategies, exploring their importance and effectiveness in building a greener, more resilient future.
Understanding Sustainable Site Development:
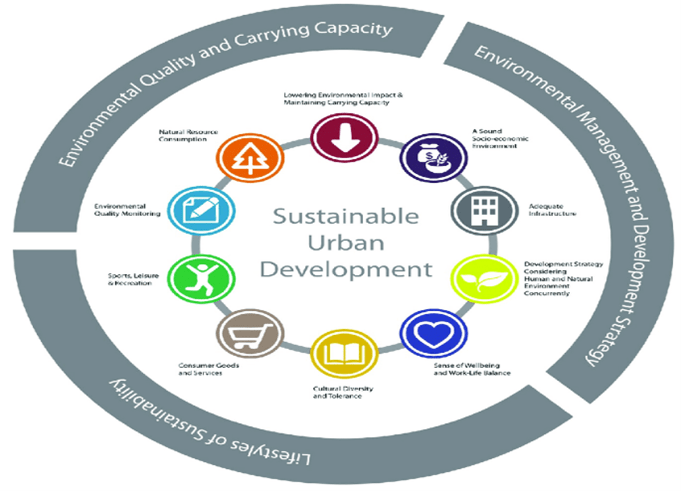
Sustainable site development involves the integration of environmental, social, and economic considerations into the planning and design of built environments. It aims to minimize the ecological footprint of development projects while maximizing benefits for both people and the planet. Key principles guiding sustainable site development include:
1. Preservation of Natural Resources: This involves protecting existing vegetation, water bodies, and wildlife habitats, as well as minimizing soil erosion and preserving natural topography. By conserving these resources, developers can maintain ecosystem services, promote biodiversity, and mitigate the impacts of development on the surrounding environment.
2. Efficient Land Use and Infrastructure: Sustainable site development emphasizes compact, mixed-use development patterns that reduce the need for sprawling infrastructure and transportation networks. By prioritizing infill development and brownfield redevelopment, developers can minimize land consumption, preserve agricultural land, and promote walkability and transit-oriented development.
3. Stormwater Management: Effective stormwater management is essential for preventing water pollution, reducing flood risks, and replenishing groundwater supplies. Sustainable site development incorporates green infrastructure practices such as rain gardens, permeable pavements, and green roofs to capture and treat stormwater onsite, mimicking natural hydrological processes and reducing reliance on traditional stormwater infrastructure.
4. Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Integrating energy-efficient design principles and renewable energy technologies into site development can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Strategies such as passive solar design, high-performance building envelopes, and onsite renewable energy generation (e.g., solar panels, wind turbines) help minimize the carbon footprint of buildings and infrastructure.
5. Social Equity and Community Engagement: Sustainable site development prioritizes equitable access to resources, amenities, and opportunities for all members of society. Engaging stakeholders in the planning and design process, fostering inclusive public spaces, and supporting affordable housing initiatives are integral to creating vibrant, socially cohesive communities.
Effective Sustainable Site Development Strategies:
Several strategies can be employed to achieve sustainable site development objectives effectively:
1. Site Analysis and Planning: Conducting comprehensive site assessments to identify environmental constraints, sensitive areas, and opportunities for conservation and enhancement is essential. Integrating this information into the planning process enables developers to make informed decisions that minimize environmental impact and maximize sustainability benefits.
2. Green Infrastructure Integration: Incorporating green infrastructure elements such as bioswales, rain gardens, and vegetated swales into site design helps manage stormwater runoff, improve water quality, and enhance biodiversity. These nature-based solutions not only provide ecological benefits but also contribute to the aesthetic and recreational value of developments.
3. Low-Impact Development Techniques: Adopting low-impact development (LID) techniques such as permeable paving, rainwater harvesting, and native landscaping can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of development projects. LID practices mimic natural hydrological processes, allowing for the infiltration, filtration, and storage of stormwater onsite.
4. Sustainable Materials and Construction Practices: Selecting environmentally preferable materials, such as recycled content products, sustainably sourced wood, and low-emission building materials, can reduce the embodied carbon and ecological footprint of construction projects. Additionally, implementing construction best practices such as waste reduction, energy-efficient construction methods, and pollution prevention measures further enhances sustainability performance.
5. Green Building Certification Programs: Engaging with green building certification programs such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) provides a framework for achieving and recognizing sustainable site development achievements. These programs offer guidelines, performance benchmarks, and third-party verification mechanisms to support the implementation of sustainable design and construction practices.
Conclusion: