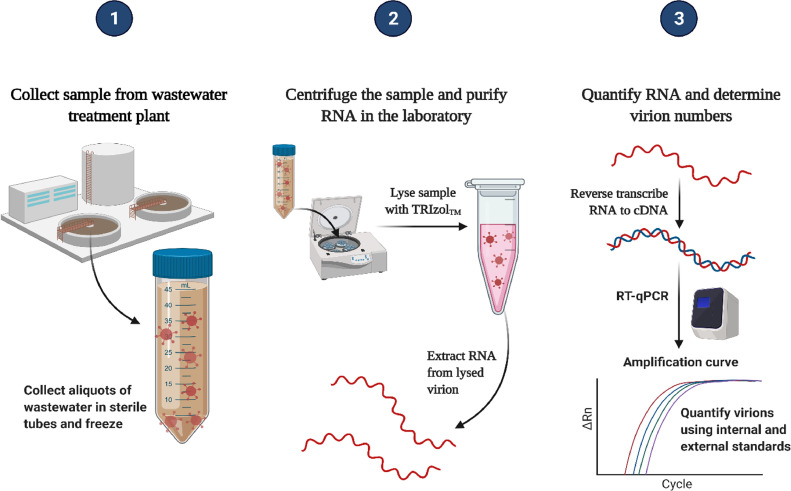
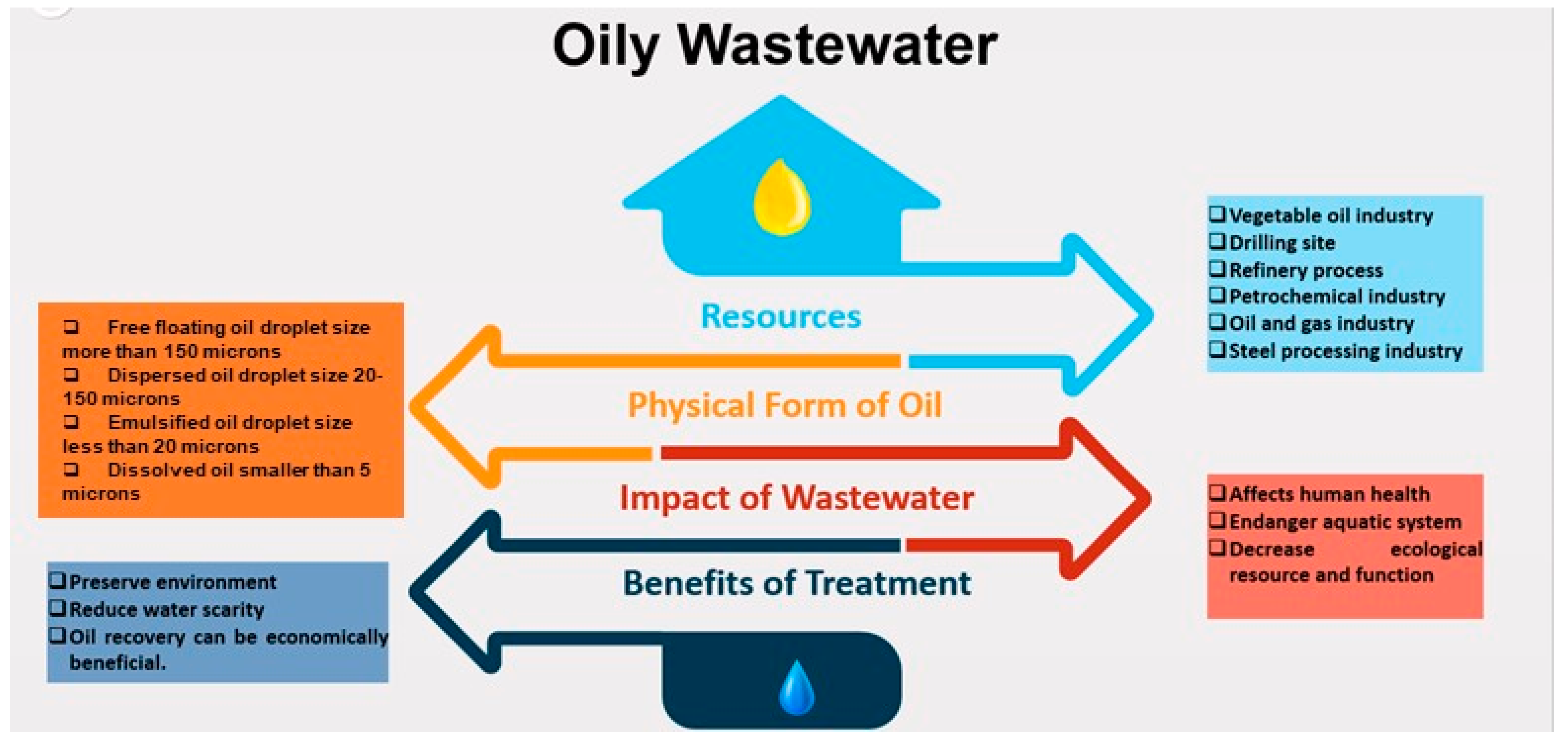
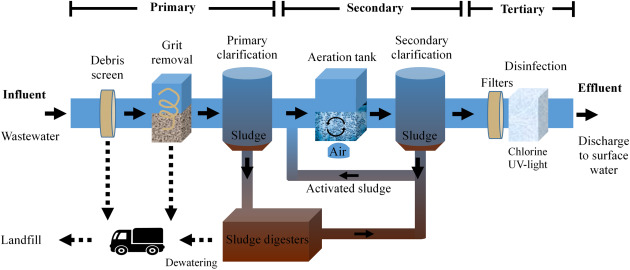
Introduction:
Wastewater treatment plays a critical role in protecting public health and the environment by removing contaminants from wastewater before it is discharged back into water bodies or reused. In recent years, advancements in technology have revolutionized wastewater treatment processes, making them more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. In this blog post, we will explore some of the cutting-edge innovations that are transforming wastewater treatment and paving the way for a more sustainable future.
1. Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs):
Membrane bioreactors combine biological treatment processes with membrane filtration to achieve high-quality effluent in a compact footprint. MBRs use microfiltration or ultrafiltration membranes to separate solids and microorganisms from wastewater, producing a permeate that is free of contaminants. This technology offers several advantages over conventional treatment systems, including higher removal efficiencies, reduced sludge production, and enhanced resistance to shock loads and fluctuations in influent quality.
2. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs):
Advanced oxidation processes involve the generation of highly reactive oxidizing agents, such as hydroxyl radicals, to degrade organic and inorganic pollutants in wastewater. AOPs can effectively remove recalcitrant contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and emerging pollutants, that are not easily biodegradable. Common AOPs include ozonation, ultraviolet (UV) photolysis, and electrochemical oxidation, which can be used alone or in combination with other treatment technologies to achieve desired effluent quality standards.
3. Membrane Distillation (MD):
Membrane distillation is an emerging membrane-based technology that utilizes hydrophobic membranes to separate water vapor from liquid streams through a thermally driven process. In wastewater treatment applications, MD can be used for concentration, purification, and resource recovery, such as the production of high-quality water from brine streams or the recovery of valuable nutrients from wastewater. MD offers several advantages, including high selectivity, low fouling propensity, and the ability to operate at low temperatures, making it suitable for treating challenging wastewater streams.
4. Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR):
Biological nutrient removal processes are designed to remove nitrogen and phosphorus compounds from wastewater through microbial metabolism. Traditional BNR processes, such as the activated sludge process and sequencing batch reactor (SBR), have been widely used for nutrient removal. However, advancements in process control, microbial ecology, and molecular biology have led to the development of more efficient and sustainable BNR technologies, such as enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR), nitritation-denitritation, and anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox).
5. Resource Recovery and Reuse:
Advancements in wastewater treatment technologies have enabled the recovery of valuable resources, such as energy, nutrients, and water, from wastewater streams. Anaerobic digestion, for example, can be used to produce biogas (methane) from organic matter in wastewater, which can be used for heat and power generation. Additionally, nutrient recovery technologies, such as struvite precipitation and biological nutrient removal, allow for the extraction of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater for use as fertilizer or other industrial applications. Water reuse and recycling technologies, such as membrane filtration and advanced oxidation, enable the production of high-quality reclaimed water for non-potable applications, such as irrigation, industrial processes, and groundwater recharge.
Conclusion: