Introduction:
Water scarcity is a pressing global challenge, exacerbated by population growth, urbanization, climate change, and inefficient water management practices. Civil engineers play a critical role in developing innovative solutions to address water scarcity, ranging from efficient water supply systems to sustainable water management strategies. In this blog, we explore the multifaceted nature of water scarcity and highlight civil engineering solutions that can help mitigate its impacts.
Understanding Water Scarcity:
Water scarcity occurs when demand for water exceeds available supply, leading to inadequate access to clean water for drinking, sanitation, agriculture, and industry. Factors contributing to water scarcity include population growth, unsustainable water use practices, pollution, deforestation, and climate variability.
Civil Engineering Solutions:
1. Water Recycling and Reuse:
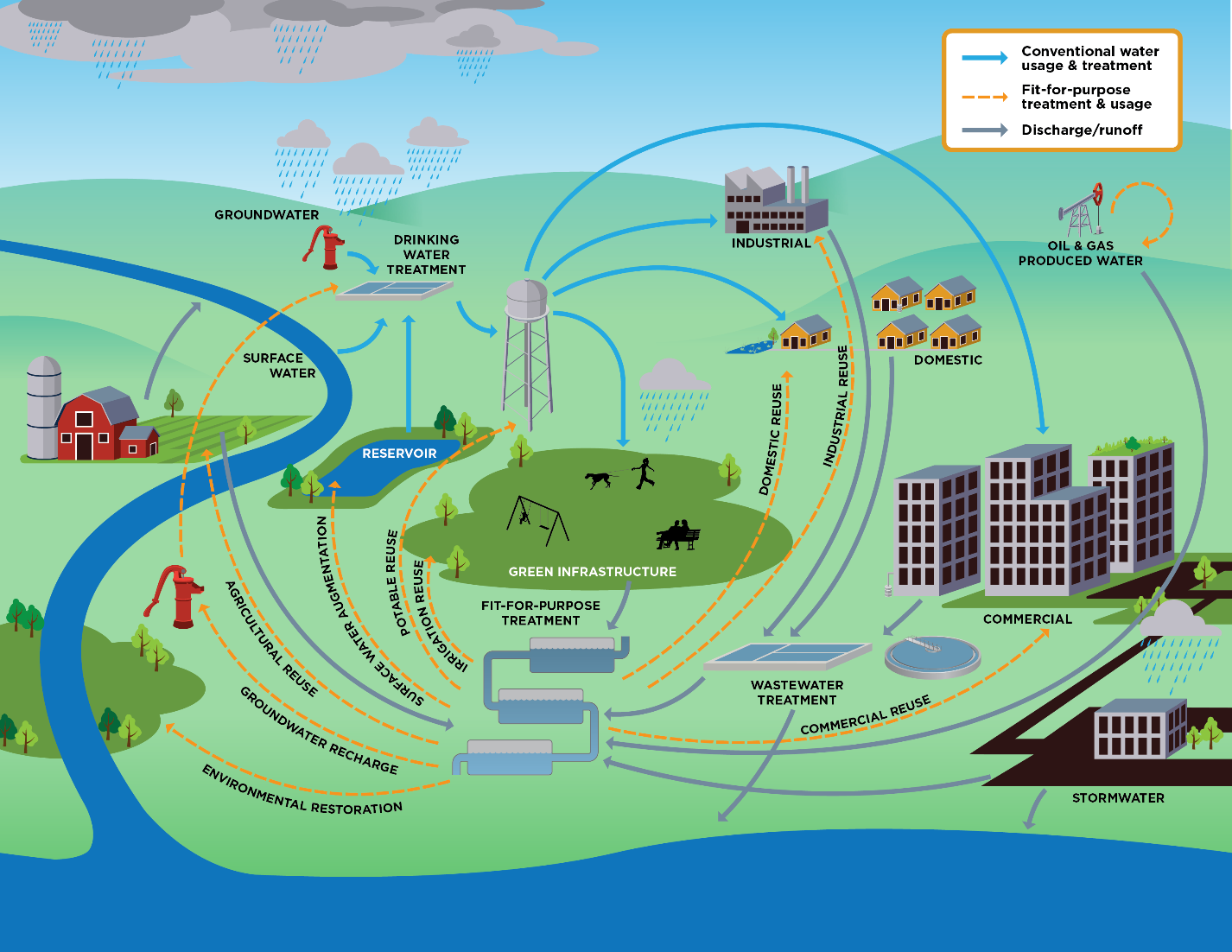
– Civil engineers develop water recycling and reuse systems to treat wastewater and greywater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, industrial processes, and toilet flushing.
– Advanced treatment technologies, including membrane filtration, UV disinfection, and reverse osmosis, remove contaminants and pathogens, producing high-quality recycled water for various applications.
2. Desalination:
– Desalination technologies, such as reverse osmosis and distillation, convert seawater or brackish water into potable water by removing salt and other impurities.
– Civil engineers design and construct desalination plants, optimizing process efficiency, energy consumption, and environmental sustainability to ensure cost-effective and reliable water supply.
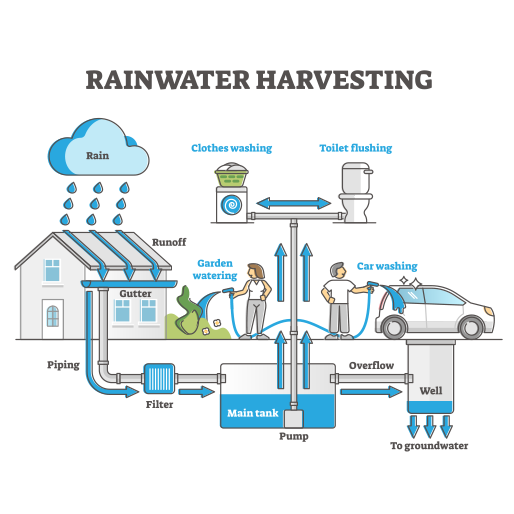
3. Rainwater Harvesting:
– Rainwater harvesting systems capture and store rainwater runoff from rooftops, parking lots, and other impermeable surfaces for later use.
– Civil engineers design rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store rainwater in tanks or cisterns, supplementing conventional water sources for irrigation, landscaping, and non-potable household uses
4. Efficient Irrigation Systems:
– Civil engineers design efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation and micro-sprinklers, to minimize water loss and optimize water use in agriculture.
– Smart irrigation technologies, including soil moisture sensors, weather-based controllers, and remote monitoring systems, enable precise irrigation scheduling and water conservation.
5. Aquifer Recharge and Groundwater Management:
– Civil engineers implement aquifer recharge and groundwater management strategies to replenish depleted aquifers and sustain groundwater resources.
– Managed aquifer recharge (MAR) techniques, such as infiltration basins, injection wells, and recharge ponds, enhance natural recharge processes and restore groundwater levels.
6. Water Demand Management:
– Civil engineers develop water demand management programs to promote water conservation, efficiency, and behavioral change among consumers, industries, and institutions.
– Demand-side management measures, including water conservation incentives, public education campaigns, and water-efficient appliances, help reduce water consumption and alleviate pressure on water supplies.
Case Studies:
1. Singapore NEWater: Singapore’s NEWater program involves treating wastewater to ultra-pure standards using advanced membrane technologies, providing a sustainable source of high-quality reclaimed water for potable use.
2. Israel’s Desalination Plants: Israel’s extensive network of desalination plants, coupled with water recycling and conservation measures, has helped alleviate water scarcity and ensure water security in arid regions.
Conclusion: