It’s critical to remain on top of technological developments in the ever changing field of civil engineering. One such invention that has revolutionized the way civil engineers plan, design, build, and oversee infrastructure projects is Building Information Modeling (BIM).
We will explore BIM and its uses in civil engineering in this blog, with an emphasis on bridges, roads, and other structures.
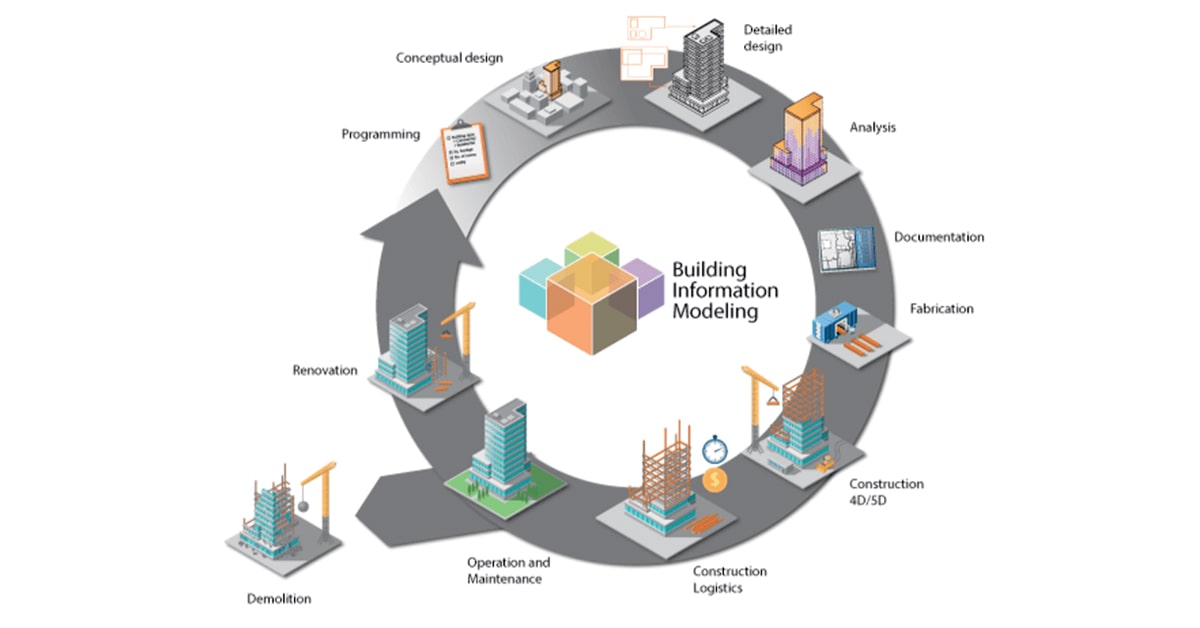
Let’s define BIM before moving on to its applications. First off, a building or infrastructure’s functional and physical attributes are represented digitally in a building information model (BIM). It’s more than simply a 3D model; it’s an extensive information library that addresses every aspect of design, construction, operation, and maintenance. BIM enables each and every project participant to
Applications of BIM in Civil Engineering
Planning and Design:
Design is revolutionized by BIM. Engineers are better able to visualize the project because they can produce precise 3D models of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. This improves decision-making since possible problems may be found and fixed early in the design process, saving money on expensive changes down the road.
Working together:
BIM encourages cooperation amongst project participants. The same data-rich model is accessible to architects, engineers, contractors, and owners as well, promoting improved collaboration and communication. Better project outcomes and more seamless project execution result from this.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting:
By offering a thorough analysis of the materials and quantities, BIM helps with precise cost estimation. Better budgeting and a lower chance of expense overruns are made possible by this.
Construction Management:
Task sequencing and scheduling can be done using BIM during construction. It helps make sure projects are completed on schedule and within budget by streamlining the construction process, monitoring advancement, and spotting possible problems.
Maintenance and Operations:
BIM isn’t limited to the building stage. As long as the infrastructure is in place, it will be valuable. Maintenance teams can obtain information about the components of the structure and identify maintenance requirements by utilizing the BIM model.
Particular Uses for Bridges and Roads
Alignment and Grading: By accounting for variables like topography, drainage, and environmental concerns, BIM can optimize road alignments and grading. This guarantees roads are sustainable as well as functional.
Bridge build:
Engineers can utilize BIM to build intricate bridge designs, which facilitates the visualization of load distribution and stress analysis. In order to make sure that all the parts work together perfectly, it also helps with clash detection.
Traffic Simulation:
Road system efficiency may be assessed and required modifications to enhance traffic flow can be made using data from traffic simulations, which BIM can incorporate.
Asset Management:
By giving precise information on the state of structures and forecasting repair requirements, BIM assists with asset management for currently in use roads and bridges.
Autodesk’s Revit is a flexible BIM program that is mostly used for structural and architectural design, but it may also be used for civil engineering projects because of its ability to integrate with other Autodesk products.
Master CAD Civil 3D:
AutoCAD Civil 3D is a well-liked BIM application for civil engineering and design. It is well known for its proficiency in organizing, managing, and supervising civil engineering projects.
Revit: Autodesk’s Flexible BIM
Transportation, utilities, and construction are just a few of the civil engineering fields that employ Bentley MicroStation, a BIM and CAD program.
Tekla Structures:
Tekla Structures is mainly used in structural engineering, but it may also be used in civil engineering to design and detail steel and concrete structures.
Infra Works:
Designed specifically for civil infrastructure projects, Infra Works from Autodesk facilitates collaboration, early design, and visualization.
Civil 3D:
AutoCAD Civil 3D is a specialized version of AutoCAD designed for projects related to land development, transportation, and the environment.
All plan Engineering is a BIM software that provides tools for design, modelling, and documentation for civil engineering and infrastructure projects.
Bentley’s Open Roads software is intended for civil engineers who are involved in transportation and road design projects. It offers extensive modelling and analytic functionalities.
Civil Site Design (CSD).
HEC-RAS: The Hydrologic Engineering Centre’s River Analysis System (HEC-RAS) is a vital tool for hydraulic and floodplain modelling, which is a critical component of many civil engineering projects, despite not being a standard BIM program.
SAP2000: Although its main application is in structural analysis, SAP2000 may also be used in civil engineering to analyze and design civil constructions such as bridges.