Introduction:
In an era where technology is rapidly transforming our lives, the concept of smart cities and infrastructure emerges as a beacon of innovation and efficiency. These interconnected urban environments leverage cutting-edge technology to enhance the quality of life for residents, optimize resource utilization, and foster sustainable growth. In this blog post, we delve into the fascinating world of smart cities, exploring their key components, benefits, challenges, and the transformative impact they have on the urban landscape.
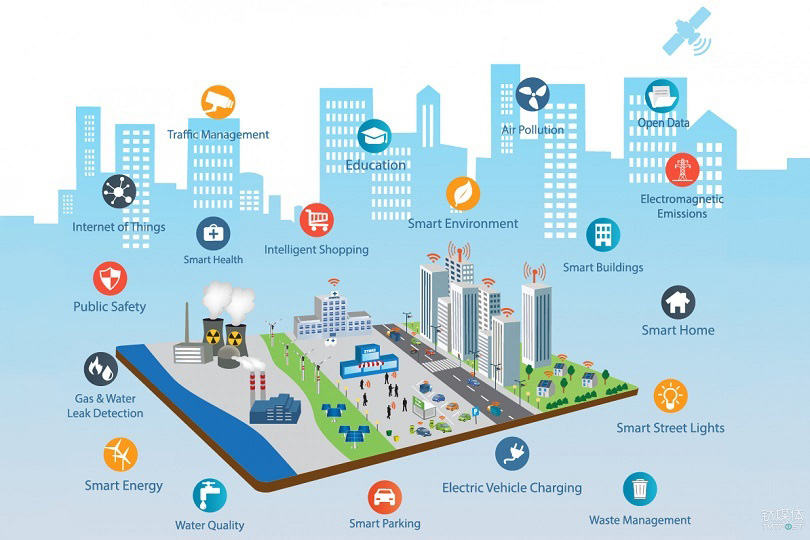
Understanding Smart Cities:
Smart cities represent a paradigm shift in urban planning, integrating Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) to manage city assets, resources, and services efficiently. At the core of smart cities lie interconnected sensors, data analytics, and robust communication networks, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis of various aspects such as traffic flow, energy consumption, waste management, and public safety.
Key Components of Smart Cities:
1. IoT Sensors: These sensors collect vast amounts of data from urban infrastructure, including traffic signals, streetlights, waste bins, and environmental conditions.
2. Data Analytics: Advanced algorithms analyze the collected data to derive actionable insights, facilitating informed decision-making by city authorities.
3. Connectivity: High-speed, reliable communication networks such as 5G enable seamless data transmission between sensors, devices, and central control systems.
4. Citizen Engagement: Smart cities emphasize citizen participation through mobile apps, interactive platforms, and community feedback mechanisms, fostering transparency and collaboration.
5. Sustainable Practices: Integration of renewable energy sources, efficient waste management systems, and green building initiatives contribute to environmental sustainability.
Benefits of Smart Cities:
1. Improved Efficiency: By optimizing resource allocation and reducing operational costs, smart cities enhance the efficiency of public services such as transportation, utilities, and emergency response.
2. Enhanced Quality of Life: Smart technologies enhance urban mobility, promote public safety, and provide better access to essential services, thereby improving the overall quality of life for residents.
3. Environmental Sustainability: From reducing carbon emissions to promoting eco-friendly practices, smart cities play a crucial role in mitigating environmental impact and fostering sustainable development.
4. Economic Growth: The deployment of smart infrastructure attracts investment, drives innovation, and stimulates economic growth by creating new job opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship.
5. Resilience and Safety: Smart cities are equipped to respond effectively to emergencies and natural disasters, ensuring the safety and well-being of residents through early warning systems and coordinated response mechanisms.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite their numerous benefits, the development and implementation of smart cities pose several challenges:
1. Privacy and Security Concerns: The proliferation of data collection raises concerns about privacy infringement and cybersecurity threats, necessitating robust safeguards and regulations.
2. Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology and digital literacy among citizens may exacerbate social disparities, underscoring the importance of inclusive policies and equitable distribution of resources.
3. Interoperability Issues: Integrating diverse systems and technologies from multiple vendors presents interoperability challenges, requiring standardized protocols and collaboration among stakeholders.
4. Financial Constraints: The upfront costs of deploying smart infrastructure and upgrading legacy systems may strain municipal budgets, necessitating innovative financing models and public-private partnerships.
5. Regulatory Hurdles: Complex regulatory frameworks and bureaucratic barriers can impede the implementation of smart city initiatives, highlighting the need for flexible governance structures and regulatory reforms.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, smart cities represent a bold vision for the future of urban living, leveraging technology to address pressing challenges and unlock new opportunities for sustainable growth and development. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing the needs of citizens, smart cities have the potential to transform our urban landscapes, making them more efficient, livable, and resilient in the face of evolving global challenges. As we navigate the complexities of urbanization in the 21st century, the journey towards smart cities promises to be both challenging and rewarding, shaping the cities of tomorrow for generations to come.