Introduction:
Infrastructure is the backbone of any society, providing essential services and facilitating economic growth. However, to ensure its longevity and optimal performance, regular maintenance and effective asset management are imperative. In this blog, we delve into the significance of infrastructure maintenance and asset management, exploring their benefits, challenges, and strategies for implementation.
Understanding Infrastructure Maintenance and Asset Management:
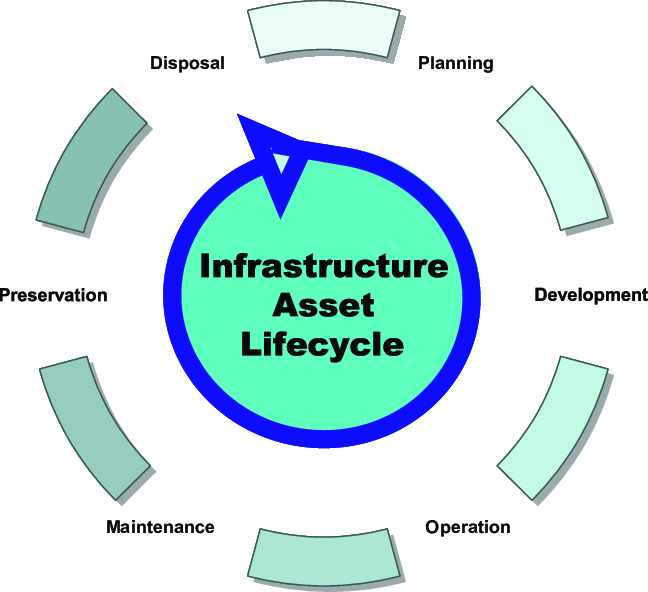
Infrastructure maintenance involves the upkeep, repair, and renewal of physical assets such as roads, bridges, water systems, buildings, and transportation networks. On the other hand, asset management focuses on optimizing the lifecycle of these assets, encompassing planning, acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal.
The Importance of Infrastructure Maintenance:
1. Safety: Regular maintenance minimizes the risk of infrastructure failures, enhancing public safety and preventing accidents.
2. Reliability: Well-maintained infrastructure operates efficiently, reducing downtime and disruptions to services.
3. Cost Savings: Proactive maintenance is often more cost-effective than reactive repairs, helping to avoid expensive emergency fixes.
4. Longevity: By addressing minor issues promptly, infrastructure assets can be preserved for longer periods, delaying the need for costly replacements.
5. Economic Growth: Reliable infrastructure attracts investment, supports commerce, and stimulates economic development in communities.
The Significance of Asset Management:
1. Optimal Resource Allocation: Asset management enables organizations to allocate resources strategically, prioritizing critical assets and optimizing maintenance schedules.
2. Risk Management: By assessing asset condition and performance, organizations can identify and mitigate risks, ensuring operational resilience.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Effective asset management helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and standards, avoiding penalties and legal liabilities.
4. Performance Monitoring: Asset management systems provide valuable data for evaluating asset performance, enabling informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
5. Sustainability: By extending the lifespan of assets and minimizing resource consumption, asset management contributes to environmental sustainability goals.
Challenges in Infrastructure Maintenance and Asset Management:
1. Funding Constraints: Limited budgets often pose challenges for infrastructure maintenance and asset management programs, necessitating prioritization and creative financing solutions.
2. Technological Complexity: Rapid advancements in technology require organizations to adopt sophisticated asset management systems and tools, which may entail significant investment and expertise.
3. Data Management: Managing vast amounts of asset data efficiently can be challenging, requiring robust data collection, storage, and analysis capabilities.
4. Aging Infrastructure: Many countries grapple with aging infrastructure systems, necessitating proactive maintenance and asset renewal to address deterioration and obsolescence.
5. Stakeholder Coordination: Effective infrastructure maintenance and asset management often require collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector entities, and communities.
Strategies for Effective Implementation:
1. Establish Clear Objectives: Define clear goals and performance metrics to guide infrastructure maintenance and asset management efforts.
2. Invest in Technology: Leverage advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), predictive analytics, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to enhance asset monitoring and decision-making.
3. Prioritize Asset Criticality: Identify critical assets and prioritize maintenance activities based on their importance to service delivery and risk exposure.
4. Adopt Preventive Maintenance: Implement preventive maintenance strategies to address issues proactively and minimize unplanned downtime.
5. Foster Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector partners, and local communities, to optimize resource allocation and achieve common objectives.
Conclusion: