Introduction:
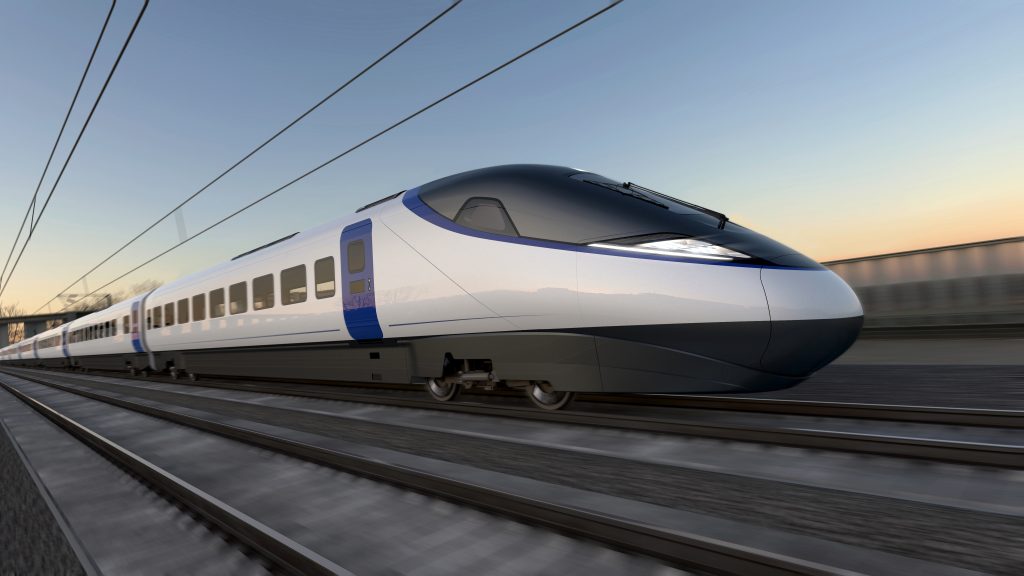
The dawn of high-speed rail heralds a new era in transportation—one defined by speed, efficiency, and connectivity. As nations across the globe invest in ambitious rail infrastructure projects, the future of high-speed rail networks promises to reshape travel patterns, spur economic development, and mitigate environmental impacts. In this blog, we embark on a journey to explore the transformative potential of high-speed rail and the innovations driving its evolution.
The Rise of High-Speed Rail:
High-speed rail has emerged as a cornerstone of sustainable transportation solutions, offering a compelling alternative to air and road travel for medium to long-distance journeys. Characterized by trains capable of reaching speeds exceeding 250 kilometers per hour (155 miles per hour) or more, high-speed rail networks epitomize efficiency and convenience, reducing travel times and enhancing connectivity between urban centres.
Key Innovations Shaping the Future:
1. Maglev Technology:
Magnetic levitation (maglev) technology represents the pinnacle of high-speed rail innovation, enabling trains to glide smoothly along tracks with minimal friction. By levitating above the guideway using electromagnetic propulsion, maglev trains achieve unprecedented speeds, surpassing those of conventional rail systems. With ongoing research and development efforts focused on maglev technology, the future holds the promise of even faster and more energy-efficient rail travel.
2. Hyperloop:
The concept of the hyperloop—an ultra-high-speed transportation system using vacuum tubes and magnetic propulsion—captivates the imagination with its potential to revolutionize intercity travel. Hyperloop pods, traveling at speeds approaching the speed of sound, offer the tantalizing prospect of near-instantaneous transit times between major cities. While still in the experimental phase, hyperloop technology embodies the spirit of innovation driving the future of high-speed rail.
3. Sustainable Infrastructure:
The future of high-speed rail networks is intrinsically linked to sustainability, with a growing emphasis on eco-friendly infrastructure and operations. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are increasingly integrated into rail systems to reduce carbon emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. Additionally, innovations in track design, materials, and construction techniques aim to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and safety.
4. Digital Connectivity and Smart Systems:
High-speed rail networks of the future will be characterized by seamless digital connectivity and smart systems that enhance passenger experience and operational efficiency. Advanced signaling systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and real-time passenger information services optimize network performance and ensure a smooth, reliable travel experience. Moreover, integrated ticketing platforms and mobile applications empower passengers with greater flexibility and convenience in planning their journeys.
The Benefits of High-Speed Rail:
1. Economic Growth and Development:
High-speed rail networks stimulate economic growth by improving regional connectivity, attracting investment, and creating employment opportunities. By facilitating faster, more efficient transportation of goods and people, high-speed rail spurs development along corridor routes and fosters economic integration between urban centres and surrounding regions.
2. Environmental Sustainability:
Compared to air and road travel, high-speed rail offers a more sustainable mode of transportation, with lower greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption per passenger-kilometer. By incentivizing modal shift from carbon-intensive modes of transport, high-speed rail contributes to climate change mitigation and air quality improvement.
3. Social and Cultural Integration:
High-speed rail networks promote social and cultural integration by bringing communities closer together and facilitating travel for leisure, tourism, and leisure. By reducing travel times and increasing accessibility, high-speed rail enhances mobility and connectivity, fostering greater social cohesion and exchange between diverse populations.
Conclusion: